Percent ionization for a weak acid (HA) is determined by the following formula: Percent ionization= [HA] ionized / [HA] initial × 100% For strong acids, ionization is nearly complete (100%) at most concentrations. However, for weak acids, the percent ionization changes significantly with concentration.Ionization or ionisation is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes.The resulting electrically charged atom or molecule is called an ion.Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with subatomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules andDivide the mass of dissociated ions by the total mass of dissociated and undissociated species; then multiply by 100 percent. You can do this by moles, too, if you use the proper coefficients from the balanced reaction. Example: When 0.5 mol of acetic acid is dissolved in enough water to make 1 liter of solution, the measured pH is 2.5. What is the percent dissociation of the acid?Acetylene: Formula & Structure 3:57 What volume (mL) of 0.20 M HCl needs to be added to 1.23 L of 0.10 M acetic acid to reduce the percent ionization to 1.00%? Assume the volume of HCl addedHow to use the formula for percentage on the left. Example #1: 25 % of 200 is ____ In this problem, of = 200, is = ?, and % = 25 We get: is/200 = 25/100 Since is in an unknown, you can replace it by y to make the problem more familiar. y/200 = 25/100 Cross multiply to get y × 100 = 200 × 25
Ionization - Wikipedia
Percent Ionization. When weak neutral acids and bases are put in water, they form ions. For example, if a weak acid like HF is place in water, it will form both the hydronium ion, H 3 O + as well as its conjugate base the fluoride ion, F-. \[{ \rm HF(aq) + H_2O(l) \rightleftharpoons H_3O^+(aq) + F^-(aq)}\]Here the portion of unionized form is 10 (pH - pKa) whereas ionized form is 1. So the percentage ionization will be % ionized= [1/ (1+10 (pH - pKa))]* 100 Alternatively, we can also rearrange the above equation by reversing the term pH-pKa into pKa-pH where we get the formula asAcid Base Equilibrium ACID IONIZATION EQUILIBRIUM 16.35 Acrylic acid, whose formula is HC 3 H 3 O 2 What is the degree (percent) ionization? K a = 1.7 x 10 4. [Ans: 4.1%] i.e., no need to use quadratic equation). 16.47 Phthalic acid, H 2 C 8 H 4 O 4the percent of ionization of the functional group in the specific environment? Identify the specific scenarios and use the Rule of Nines to calculate the percent of the functional group that would be ionized. Answer: To use the Rule of Nines, the difference between the pH and the pK a must be an integer (i.e., 1, 2, 3).

How do you calculate percent dissociation? + Example
You can calculate the percentage of ionization of an acid given its pH in the following way: Step 1: Convert pH to [H+] pH is defined as -log [H+], where [H+] is the concentration of protons in solution in moles per liter, i.e., its molarity.1) Calculate the percent dissociation of HA in a 0.10 M solution. 2) Calculate the percent dissociation of HA in a 0.010 M solution. 3) Calculate the percent dissociation of HA in a 0.0010 M solution. Solution to part one: Step #1: Calculate the [H +]: 9.2 x 10¯ 7 = [(x) (x)] / (0.10 - x) neglect the minus x x = 3.03315 x 10¯ 4 MpH scale. The pH scale (pH) is a numeric scale which is used to define how acidic or basic an aqueous solution is. It commonly ranges between 0 and 14, but can go beyond these values if sufficiently acidic/basic. pH is logarithmically and inversely related to the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The pH to H + formula that represents this relation is:% ionization = [H3O +]eq [ HA] 0 × 100 Because the ratio includes the initial concentration, the percent ionization for a solution of a given weak acid varies depending on the original concentration of the acid, and actually decreases with increasing acid concentration. Example 1: Calculation of Percent Ionization from pHPercent Ionization. mrshow Thu, 01/17/2008 - 00:17. I've been doing quite a few Acid/Base Equilibrium problems lately, asking me to solve for pH and the liking. Many problems require using the quadratic formula to solve them, but I know that if the percent ionization of the acid/base is less than 5, than I can just keep the original acid/base
Percent ionization for a vulnerable acid (HA) is determined by the following formula:
Percent ionization=[HA] ionized / [HA] preliminary × 100%
For robust acids, ionization is just about whole (100%) at maximum concentrations. However, for weak acids, the percent ionization adjustments considerably with concentration. The extra diluted the acid is, the greater percent ionization.
A definite vulnerable acid, HA, has a Ka value of 7.6×10 −7.
A) Calculate the percent ionization of HA in a 0.10 M solution. Express your resolution as a percent using two significant figures.
B) Calculate the percent ionization of HA in a nil.010 M solution. Express your answer as a percent using two important figures.
Percent Dissociation (Ionization)

Calculate the degree of ionization of 0.05 M aceti toppr.com

Percent Ionization - YouTube

How To Calculate Percent Ionization Given Molarity

Acids and Bases on a Snowy Valentine's Day

Calculation of Percentage ionization of weak electrolytes

Tang 05 ionization + kb 2
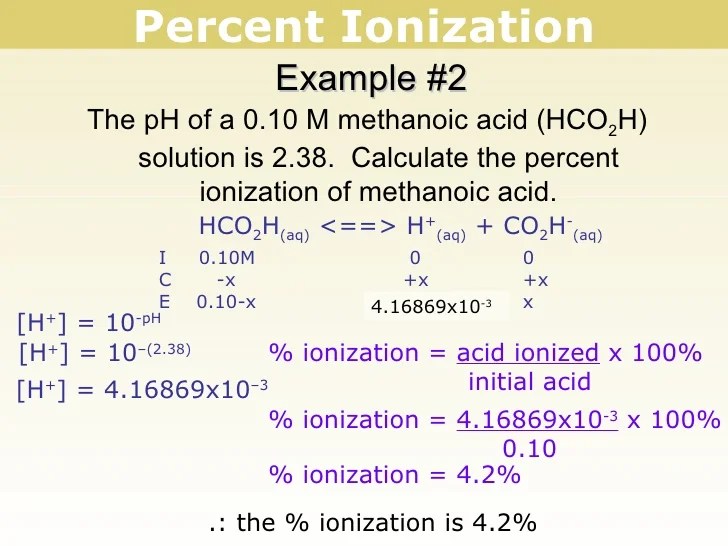
Calculate the percent ionization of formic acid (HCO2H) in ...
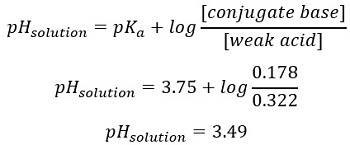
How to Calculate the Percentage of Ionization Given the pH ...

Physical and chemical properties of drug molecules ...
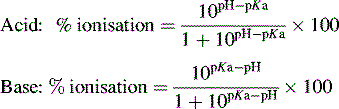
PPT - pH and K a values of Weak Acids PowerPoint ...

Ionization: Equation For Percent Ionization

Solved: Name And Write The Formula For The Conjugate Acid ...
Answered: calculate the percent ionization of… | bartleby

Solved: Calculate The Percent Ionization (the Approximatio ...
Chemical Equation For Ionization Of Acetic Acid In Water ...

How to Calculate the Percent Ionization | Sciencing

Equilibrium Equation For Ionization Of Acetic Acid ...

Solved: Calculate the percent ionization of acetic acid ...

Calculate the percent ionization of formic acid (HCO2H) in ...

Solved: Percent Lonization Percent Ionization For A Weak A ...
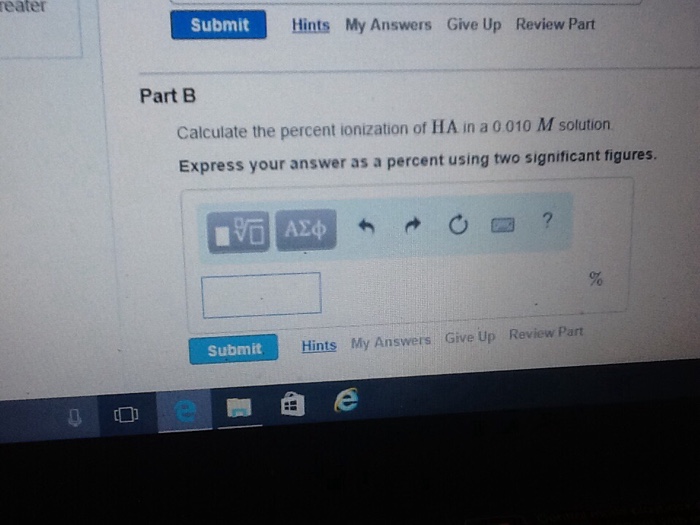
0 Comment to "ChemTeam: Calculate Percent Dissociation From PH And Ka"
Post a Comment